In December 1992 there was sent the first SMS. At that time there were several different vendors working on their first SMSCs. I was lucky enough to work later with some of the engineers involved. Anyways that is an ancient history now. Since that the SMS Service and the SMSC have become a must for every mobile network. Perhaps we can go trough the general SMSC network architecture, list some of the typical features and then to discuss the SMS evolution in 5G networks.
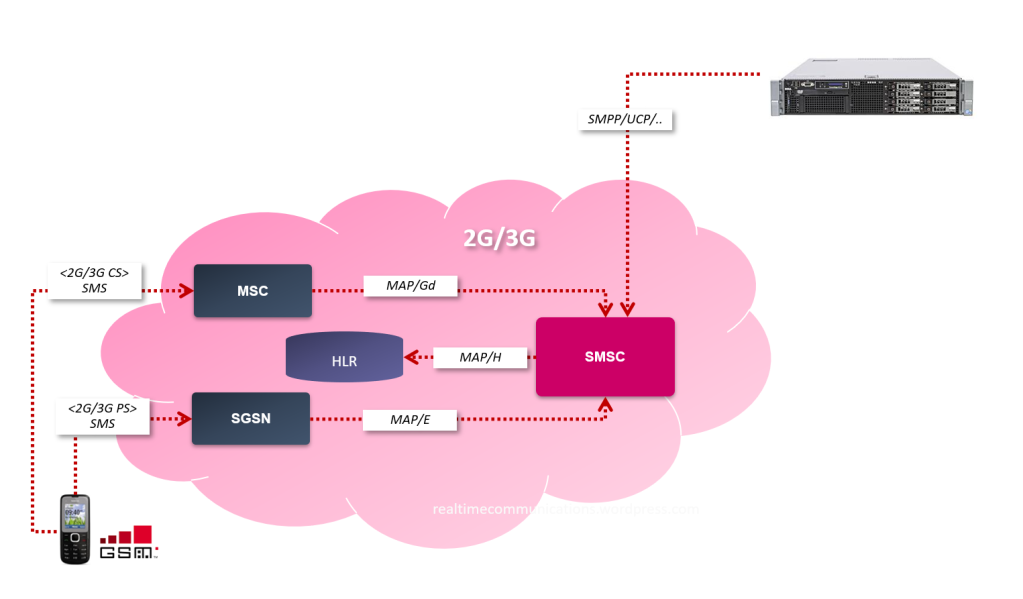
The SMSC was designed as an integral part of 2G mobile network, supporting several basic message flows, which are mostly valid even in 2022:
- Person-to-Person (P2P)
- Application-to-Person (A2P/P2A). This was a real game changer. People in late 90s were texting (and paying) as crazy to get new ringing tones, text-frames on their monochromatic displays or at least a weather forecast or bus schedule. The A2P is still a popular way how to create a significant wholesale interconnection and also valid for MIoT (Mobile Internet of Things). Last but not least we shouldn’t forget the importance of SMS in Two-Factor-Authentication (2FA).
- Technical enabler: Over the Air OTA messaging for (U)SIM provisioning. OTA is still critical for many operators. Another example is an IP session wake-up, which might be a key technical enabler for some Machine Type Communication MTC/MioT applications.